The Fascinating Properties of Fascia
“This vast network is made primarily of collagen threads, woven into an intricate, multidimensional matrix. Within this living framework, fascia helps distribute forces, maintain postural balance, and transmit movement. It is also electrically conductive, assisting in the integration and coordination of every part of the body. This electrical communication is essential for regulating cellular processes and maintaining the body’s overall functioning.”
(M.J. Porter, Founder of Fascial Dynamic Manual Therapy)
What Happens When Fascia Loses Its Freedom
When the fascia’s elasticity is compromised, the subtle fluid pressures that support metabolic processes may also be disrupted. This can impair the body’s natural instructional communication—its bio-electrical signalling—reducing efficiency in healing, movement, and self-regulation.” ( MJ Porter; Fascial Dynamic Manual Therapy)
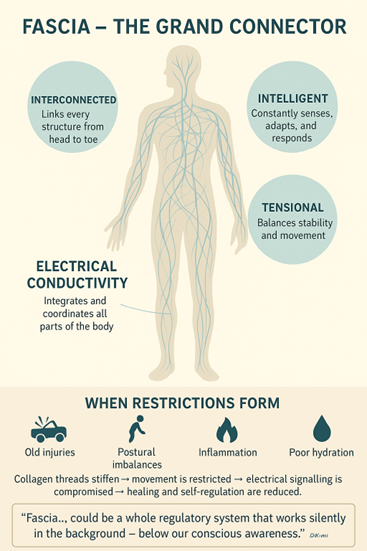
Fascia is one of the most remarkable and underappreciated systems in the human body. It is interconnected, linking every structure from head to toe; intelligent, constantly sensing and adapting; and tensional, maintaining a delicate balance that supports both stability and movement.
Deep Tensions, Widespread Effects
Restrictions in fascia can run deep, sometimes reaching into the body’s core and creating lines of tension at multiple levels. These tensions can interfere with both subtle and large-scale movements, impacting flexibility, posture, and function. Over time, these altered tensions disrupt the bio-electrical network, influencing cellular health and limiting the body’s ability to repair itself.
“Fascia, with its connections to the interior of cells and cell nucleus, and with its electronic conductor properties, could be a whole regulatory system that works silently in the background—that is, below our conscious awareness.”- Dr. Oshmann
Fascia is more than a structural tissue—it is a dynamic, sensing, communicating network that underlies your ability to move, heal, and thrive.
Fascia as a Living and Responsive System
Fascia is not just the body’s wrapping — it’s a living, breathing web that connects every part of you. It surrounds and supports your muscles, bones, organs, and nerves, creating a continuous, fluid network that allows your whole body to move and communicate as one.
Imagine this network like a woven fabric of silk and water — flexible, strong, and sensitive. When it’s healthy, fascia glides easily, letting your body move freely and gracefully. But when it becomes restricted — through injury, stress, or long periods of stillness — that fluid weave can tighten and lose its elasticity. Movement starts to feel stiff, and pain or tension may appear where the fabric has lost its gentle flow.
Fascia responds to everything — your posture, movement, hydration, emotions, and even your breath. It’s constantly adapting, listening, and adjusting to how you live in your body.
What Makes Fascia “Living”?
Old injuries, repetitive load, inflammation, chronic stress, low hydration, or poor sleep can lead to stiffening of the collagen fibres. Hyaluronic Acid (HA), a gel-like lubricant matrix that is produced by the body, surrounds every cell. HA can stiffen and form restrictions and adhesions.
Clinically, people describe morning stiffness, “stuck” ranges, diffuse ache, or pain that seems to travel. These changes reduce glide and alter sensation input.
Fascia is “living” because it’s made up of cells that sense, respond, and communicate — much like the rest of your nervous and immune systems. Within this collagen-rich web are specialized cells called fibroblasts that constantly rebuild and repair the tissue, keeping it resilient and responsive.
Tiny movement signals ripple through the fascia, like whispers across a spider’s web, allowing your body to sense changes in tension, pressure, and balance. This bioelectric communication connects every cell to its environment, helping to coordinate the body’s healing and adaptability.
When the fascia loses mobility, these signals can become muffled — like static in a conversation. But when the tissue regains its suppleness and glide, that conversation becomes clear again. Movement feels easier, pain lessens, and the body begins to reestablish its natural harmony.
What restricts fascia—and what that feels Like
Why Manual and Movement Therapies Help
Targeted loading, stretching, and manual techniques provide mechanical cues that fascia understands: rehydrating layers and stimulating fibroblast remodelling. By improving glide and tuning receptor input, therapies can downshift protective muscle tone and support the body’s self-regulation. This is one pathway by which hands-on care and intelligent movement can ease pain and restore ease.
Practical Takeaways
- Fascia is a whole-body communication and regulation system—sensory-rich, fluid-dependent, and mechano-electrically active.
- Restrictions alter mechanotransduction, fluidity, and signalling, raising pain and reducing movement efficiency.
- Intelligent loading, hands-on care, and hydration strategies help re-tune this system toward resilience.
Mechanotransduction: the process by which cells convert physical forces, like touch, pressure, or stretch, into biochemical signals that the cell can understand and respond to.
